As things stood in 2019, fast food in the U.S. was a $647.7 billion industry, and fast casual, $125.6 billion. Considering that fast food has been around for more than half a century and fast casual only started gaining momentum about a decade ago, both dining categories clearly have a major impact on the American economy as a whole, along with our individual dining enjoyment and physical health.
Despite the importance of fast food and fast casual, many people are confused about how these two dining categories are different, and some are completely unfamiliar with the phrase “fast casual.” The accompanying resource explains all of this in an easy-to-digest manner.
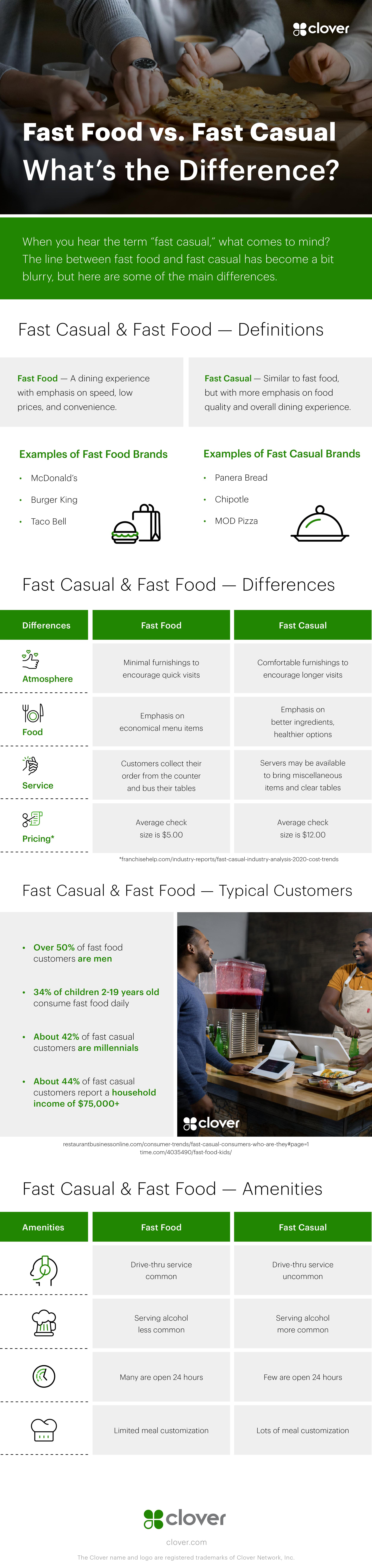
Why is it important to understand the difference between fast food and fast casual? If you’re looking for a place to eat and you have one option describing itself as fast food, and another describing itself as fast casual, you’ll be in for a much different experience depending on which way you go.
For example, expect to leave a fast food establishment with a little more money in your pocket than after a visit to a fast-casual restaurant. On the other hand, a fast-casual meal will likely give you the opportunity to customize your order and enjoy healthy ingredients; a fast food meal, as you are no doubt aware, may be a bit less healthy and customization of any kind might not be possible.
The line between fast casual and fast food is not as clear as it perhaps once was, however. For instance, due to the pandemic and for other reasons such as heightened customer demands for convenience, fast food restaurants are beginning to adopt practices such as online ordering and contactless payment similar to what many fast casual restaurants offer.
The issue of healthy food options has led fast food businesses to add healthier choices to their menus. Desires for social distancing and (again) greater convenience have contributed to the setup of drive-thru service in various fast casual locations. Nevertheless, fast food and fast casual offer significantly different dining experiences, and it’s important for consumers to understand what those differences are.
It’s also vital for fast food and fast casual business operators to help consumers understand the differences. If a consumer comes into a fast food establishment seeking a fast-casual experience, or vice versa, that consumer may be disappointed, which will make future visits less likely. Some brands, such as McDonald’s and Burger King, have been around so long that just about every consumer in the U.S. knows what to expect. However, if your business is a startup, entering a new geographic market, or is a less recognized brand, highlighting your position as a fast casual or fast food restaurant on your website and in your marketing campaigns is essential for drawing in the right consumers and building a strong, loyal customer base.
For more insights on the differences between fast food and fast casual, please continue reading. Infographic created by Clover Network.