Asian Catfish, locally known as hito to Tagalogs, paltat to Ilocanos, pantat to Cebuanos and Ilonggos, and ito to Pampangeños, is one of the most important freshwater food fishes not only in the Philippines, but in the whole of Southeast Asia. Catfish culture requires less area, can tolerate poor water quality, as well as high density stocking. In addition, disease occurrence in catfish has not been a significant problem so far.

Catfish broodstock can be obtained from lakes, rivers and other freshwater bodies. It can be stocked in earthen ponds or in concrete tanks with mud at the bottom. Catfish mature in about 6-8 months. Breeding season varies but usually starts in May.
Spawning the catfish
1. Get desired number of broodstock (at least 20 males and 50 females), and place in separate holding containers.
2. Determine the total body weight (BW) of female catfish to be spawned artificially and prepare hormones to be used. Pituitary glands, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue (LHRHa) + pimoside (PIM), Ovaprim, or Ovatide may be used. Injection dosages as administered to female broodstock are as follows:
• 1 homogenized pituitary gland/100 g BW
• 4 I.U. human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)/g BW
• 0.05 μg luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue (LHRHa) + 1 μg pimoside (PIM)/g BW
• 0.5 μL Ovaprim/g BW
• 0.2-0.5 μL Ovatide/g BW
3. Anesthetize the female catfish by placing them into a pail with 10 liters of tap water mixed with 5 mL anesthesia (2-phenoxyethanol). Pat dry the fish and inject hormone to dorsal musculature.
4. Anesthetize males, pat dry, and cut up the middle part to take out the pair of testes-seminal vesicles. Place this in a Petri dish, rinse with 0.9% NaCl, blot-dry, transfer to a clean dish, macerate, and add 0.9% NaCl to obtain milt solution.
5. Press the abdomen to strip eggs into a clean, dry bowl or basin. Pour the milt solution into the bowl or basin and mix for 30 to 60 seconds using a feather. Add 5 mL tap water, mix further to ensure fertilization and transfer fertilized eggs to a scoop net. Wash with running tap water to remove excess milt. Spread the eggs on a net tray inside a flow- through hatching trough or basin. Maintain water level of about 10 cm inside the trough or basin.
6. Observe if most larvae have hatched 24-30 hours after fertilization and incubation. Feed larvae with natural food organisms like Moina.
Raising the larvae
1. Transfer 4-6 day-old larvae in bigger tanks with 10-15 cm water level. Aerate mildly, place shelters at the bottom, and feed larvae with newly hatched Artemia nauplii at 10 individuals/mL twice a day. Change about 30% of the water in the larval rearing tanks daily.
2. Feed 7-10 day-old larvae with Moina or Daphnia at 5-10 individuals/mL for another 4 days; otherwise, continue feeding Artemia nauplii. Start feeding the larvae with catfish feeds in the morning of day 10 and give natural food organisms in the afternoon. Change 50% of water daily from hereon.
3. Continue giving catfish feeds until larvae can be transferred to nursery system on day 15
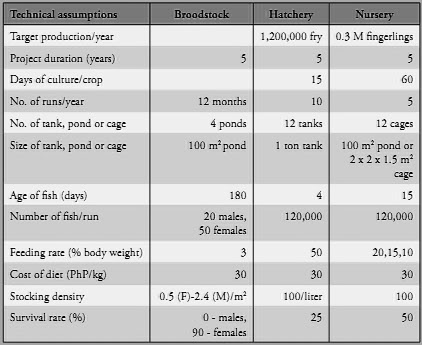
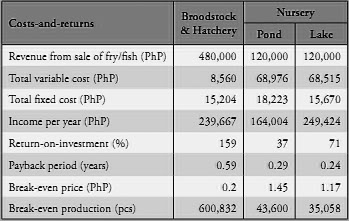
Financial Indicators
For more information, contact:
Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center
AQUACULTURE DEPARTMENT
www.seafdec.org.ph
© SEAFDEC/AQD 2009
I want to buy ovaprim hormone for catfish spawn ing