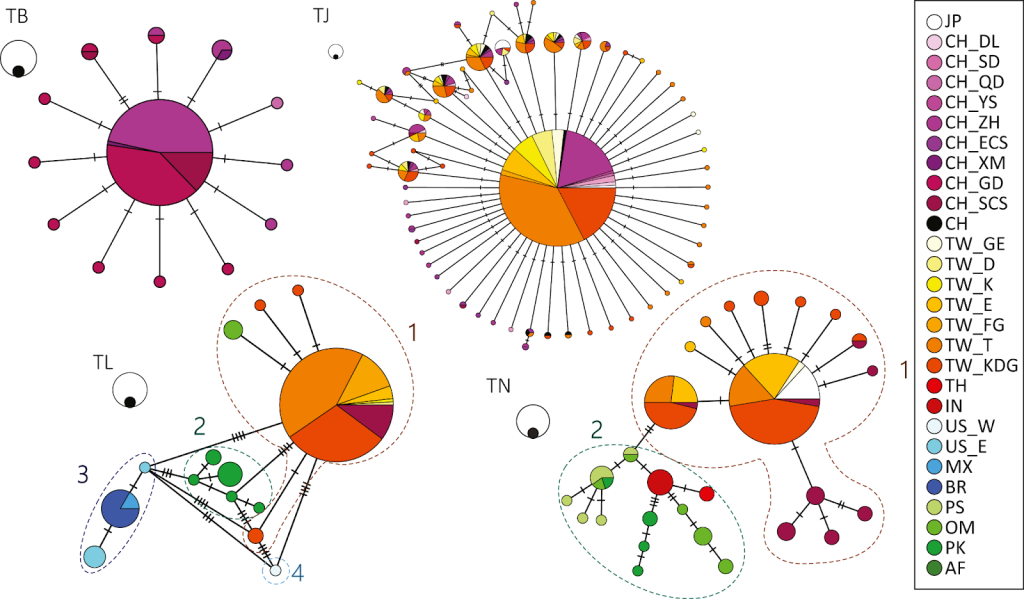
Haplotype variety, the version in the aggregate of alleles on a single chromosome, plays a vital function in expertise the genetic diversity and evolutionary procedures in non-human species. The look at haplotype diversity gives treasured insights into populace genetics, evolutionary records, and adaptation of species to their environments. By means of inspecting haplotype range in non-human species, researchers can gain a deeper knowledge of the mechanisms using genetic version and the evolutionary forces shaping biodiversity.
Evolutionary Forces Shaping Genetic Variation
Evolutionary procedures, which include herbal choice, genetic float, mutation, and gene flow, contribute to the generation and maintenance of haplotype range within populations of non-human species. Those processes influence the distribution of genetic variants throughout different geographic areas and can provide clues about the ancient demography and evolutionary history of species. know-how haplotype diversity in non-human species can shed light on the genetic basis of model, speciation, and the reaction of populations to environmental adjustments.
One of the key insights received from reading the haplotype range in non-human species is the identity of evolutionary forces that shape genetic version. Natural selection, for example, can power the spread of beneficial haplotypes related to adaptive developments, together with resistance to disease or environmental stressors. By studying haplotype variety, researchers can locate signatures of high quality choice and infer the genetic basis of adaptive evolution in non-human species.
Historical Demography and Population Dynamics
Moreover, haplotype diversity affords a window into the historic demography and population dynamics of non-human species. patterns of haplotype variety can screen beyond demographic occasions, such as populace expansions, contractions, or migrations. As an example, the identity of wonderful haplotype clusters in extraordinary geographic regions can imply ancient isolation and subsequent divergence of populations. By reconstructing the evolutionary history of non-human species using haplotype facts, researchers can elucidate the factors which have shaped the modern-day genetic structure and variety of populations.
Conservation Implications of Haplotype Diversity
Similarly, a look at the haplotype range in non-human species can make contributions to conservation efforts by supplying insights into the genetic health and viability of populations. Low haplotype diversity and high levels of inbreeding, as an instance, can be indicative of small population sizes and genetic bottlenecks, which might be of problem for the long-time period survival of species. By way of assessing haplotype range, conservation biologists can perceive populations at risk and develop centered conservation strategies to keep genetic diversity and prevent the lack of particular haplotypes.
Technological Advancements and Genomic Tools
Advances in genomic technology have revolutionized the study of haplotype range in non-human species, permitting researchers to have a look at genetic variation at remarkable resolution. high-throughput sequencing and genotyping techniques have facilitated the comprehensive analysis of haplotype range throughout the genomes of numerous non-human species, offering a wealth of information for expert evolutionary tactics. Furthermore, the improvement of bioinformatics tools and populace genetic models has allowed for the strong inference of demographic history, selection signatures, and phylogeographic styles from haplotype statistics.
Case Studies: Insights from Haplotype Diversity
Case studies of haplotype diversity in non-human species have yielded precious insights into evolutionary approaches and populace genetics. For example, studies at the haplotype variety of the cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) has found a lack of genetic variant, probably resulting from a historic populace bottleneck. This low haplotype diversity has raised issues about the genetic fitness and adaptive capacity of cheetah populations, highlighting the significance of genetic monitoring and conservation efforts for this iconic species.
Further, studies of haplotype variety in non-human primates, which includes chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and gorillas (Gorilla gorilla), have provided important insights into their evolutionary history and populace structure. By means of analyzing haplotype facts from a couple of populations, researchers have uncovered styles of genetic differentiation, gene go with the flow, and demographic adjustments, shedding light on the evolutionary processes that have shaped the diversity of these species.
Adaptive Evolution and Environmental Change
Furthermore, investigations into the haplotype variety of non-human species in reaction to environmental exchange have discovered the function of adaptive evolution in shaping genetic variation. For instance, studies of haplotype variety in fish populations uncovered to exclusive environmental conditions have recognized genomic regions related to neighborhood edition, imparting evidence of the genetic foundation of ecological divergence and the capability for fast evolutionary responses to environmental demanding situations.
Future Prospects: Integrating Genomic and Environmental Data
Looking ahead, take a look at the haplotype range in non-human species holds promise for addressing fundamental questions in evolutionary biology, ecology, and conservation. By integrating genomic records with ecological and environmental records, researchers can elucidate the interplay among genetic variant, natural choice, and environmental factors in shaping the evolutionary trajectories of non-human species. This integrative method can offer a comprehensive understanding of the adaptive capability and resilience of populations inside the face of ongoing environmental modifications.
Concluding Remarks: Significance of Haplotype Diversity
In the end, haplotype diversity in non-human species offers treasured insights into evolutionary techniques, population genetics, and adaptation. By examining styles of haplotype range, researchers can find the genetic signatures of evolutionary forces, reconstruct the demographic records of populations, and inform conservation strategies. The observation of haplotype diversity, facilitated by means of advances in genomic technologies and analytical techniques, has the capacity to deepen our understanding of the genetic foundation of biodiversity and the mechanisms driving evolutionary trade in non-human species.
Read more: Scientific Asia News
